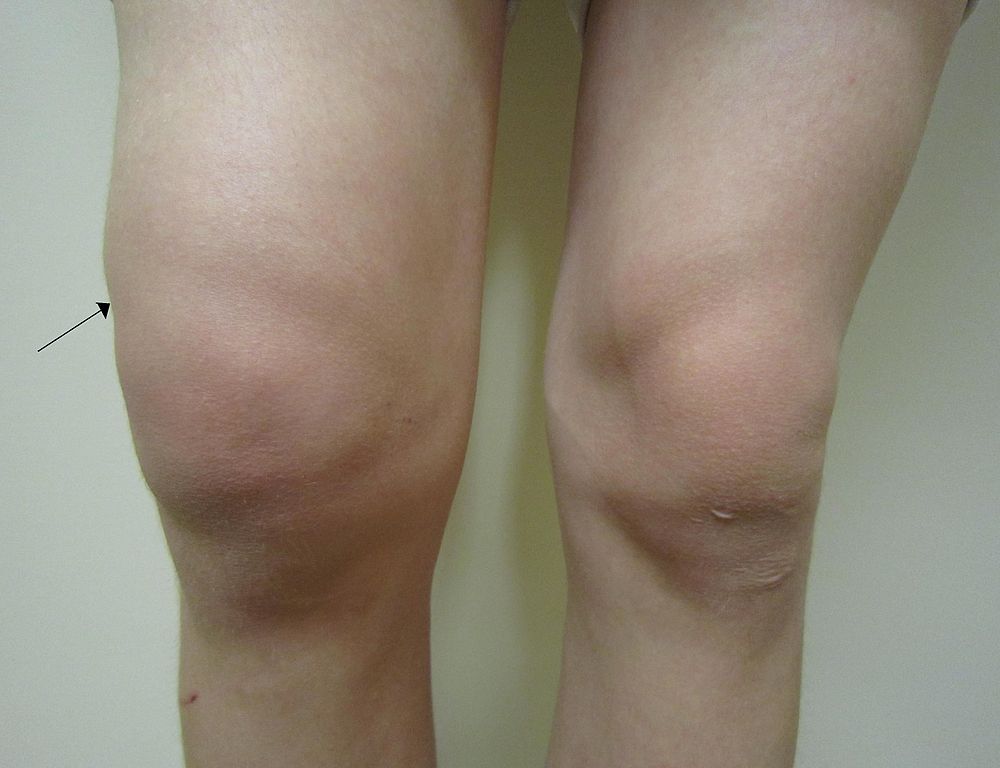
For both youngsters and adults, a swollen knee (also referred to as knee effusion) can be frustrating. Not only can swelling result in extreme pain and inflammation, but it can also distort an individual’s range of motion in the affected leg. If left untreated, the swelling can worsen to the extent that the knee can become unworkable. Some of the conditions that cause swelling range from mild to chronic and treatments also vary.
Here’s a look at some of the more typical causes:
1. Synovitis
Synovitis occurs when the synovium membrane which lubricates and surrounds the inner lining of your knee joint becomes inflamed. Its main purpose is to build synovial fluid, which helps lubricate and nurture the joint. Also, there’s a fold inside the synovium called the plica that is present near the kneecap. When a person’s kneecap goes forth and back, it can pinch the fold, resulting in pain. One of the best treatments for synovitis is a minimally invasive arthroscopic procedure to address pain and swelling. It involves the use of a small incision and the placement of a scope and a specific surgical instrument to remove the impaired fold and synovial tissue.
2. Baker’s Cyst
Swelling behind the knee can occur due to a Baker’s cyst. The condition causes the synovial fluid (that is found inside the knee joint) to accumulate at the opposite part of the knee. Baker’s cyst usually occurs if there is an underlying problem with an individual’s knee such as arthritis. Symptoms can include swelling, pain and tightness at the back of the knee. Rarely, the condition can rupture and lead to symptoms similar to a DVT (deep vein thrombosis). Sufferers should treat Baker’s Cyst at home with the R.I.C.E (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) procedure and also consult with their physician, who can exclude other potential diagnoses.
3. Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis is a germ-related infection that causes the knee joint to become inflamed and swollen. The infection can result from bacteria that travel via your bloodstream from another area of your body. It can also be caused by a high-impact injury that delivers microorganisms directly to the knee joint. Seniors and infants are most susceptible to this condition. Apart from swelling, septic arthritis can cause extreme discomfort in the knee. And if left untreated, it can quickly damage the bone as well as the cartilage within the joint. Antibiotics are used to address the condition. If the joint fluid keeps building up, a needle may be inserted to withdraw the synovial fluid from the joint.
4. Gout
Gout is actually a mild type of arthritis that commonly affects the right or left knee of individuals. It may lead to a sudden burning sensation in one of your knee joints, or swelling around the kneecap. Gout attacks can repeatedly occur if left untreated and cause long-term damage to your bones, soft tissues and tendons. Your odds of getting knee gout are higher if you have excess levels of uric acid in your bloodstream. That’s because excess uric acid turns into crystals, which form in the joints. The methods of treatment can vary on the severity of gout. Your doctor may give you a corticosteroids’ shot, and prescribe other medications that are specially manufactured to reduce uric acid. Physical activity that strengthens the knee joint may also work in your favor.
Whatever the cause in your case, seek treatment before what looks like a mild condition becomes a grave medical ailment.